GERMINATION OF SEED
The life cycle of plants and trees starts with the germination of seeds. Plants and trees produce seeds and seeds develop into new plants . The cycle thus continues keeping the species alive and continuing.
Introduction to Factors affecting Germination of seedsGermination is defineds as sprouting of seeds, a sprout, a spore, or additional reproductive body, regularly done after a period of dormancy.
Availability of water, health of the seeds, time, temperature and heat, presence of oxygen, and exposures to light play an important role in the germination process.
Stages in GerminationImbibition:
The initial step in the development of seed germination is to absorb water or imbibition The seed absorbs water and as a result it swells. The swelling of seed causes the seed coat to rupture and allows the radicles to move downward forming the root.
Respiration:
When the seed absorbs water, it also respires. While in the beginning the respiration is anaerobic and later it becomes aerobic.
Factors Affecting Germination Process of Seeds:
- Temperature: Extremely low or cold temperature is not favorable for seed germination. They prefer higher temperatures. The germination rate of seed is directly proportional to the rise in temperature.
- Moisture or water: Dry seeds do not germinate. Water is an essential factor to trigger off the process of seed germination.
- Soil: During growth, seeds require mineral elements for further growth which is obtained from the soil.
- Light: For seed germination light is not essential in the early stages of germination but plays a main role in the later stages of the life cycle of plants.
- Viability of the seeds: After the seeds are formed, they remain viable up to certain period which may vary from plant to plant or seed to seed. Many sees die or incapable of supporting growth after a certain period of time.
- Dormancy period: Many seeds do not germinate abruptly after they are produced . Certain seeds undergoe a resting time through which they stay dormant and germinate when conditions are favourable. Preence of growth inhibitors like abscisic acid induce dormancy in seeds.
- Thinness or thickness of seed coat: Different seeds have varying degrees of thickness to enable the seeds to remain feasible. Seeds with a thin seed coat tend to germinate faster than those with thicker seed coats.
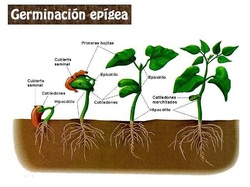
The first thing to come out is the main root. The skin or seed coat starts to split and the tiny shoot straightens, carrying the cotyledons with it. This is called radicle or the main root which grows bigger. Root hairs appear as the growth takes place. Gradually, first leaves called plumule starts growing which forms the shoot in initial stages. To grow, the seed's growing conditions usually have to be damp, warm, and dark, with moderate soil. A dry seed will stay dormant unless the conditions are favorable. Later, seeds germinate supporting a new life.
